The Unbreakable Foundation of Modern Digital Security and Trust
In an age where data is the most valuable corporate asset, the process of safeguarding it has become a non-negotiable aspect of business operations. The fundamental technology underpinning this protection is Data Encryption, the method of converting plaintext data into an unreadable format known as ciphertext. Only individuals with the correct cryptographic key can decipher the information, rendering it useless to unauthorized parties. This principle is the bedrock of modern cybersecurity, providing a critical last line of defense against data breaches, insider threats, and cyberattacks.
As organizations collect and transmit unprecedented volumes of sensitive information—from personal identifiable information (PII) to intellectual property—encryption serves as the essential tool to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and compliance, building a foundation of trust with customers and partners in an increasingly interconnected digital world. The Data Encryption Market size is anticipated to expand to USD 40.2 billion by 2032, registering a compound annual growth rate of 16% during the 2024-2032 forecast period.
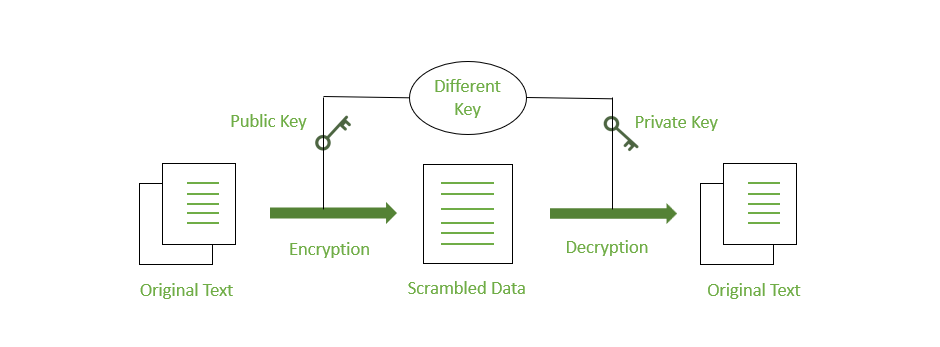
Encryption methodologies are broadly categorized into two types: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key for both encrypting and decrypting data. It is known for its speed and efficiency, making it ideal for encrypting large volumes of data, such as entire hard drives or databases. Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption, which can be shared widely, and a private key for decryption, which is kept secret. While slower than its symmetric counterpart, it is foundational for secure communication and digital signatures, enabling secure transactions over the internet via protocols like TLS/SSL. Most modern security systems use a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of both methods to create a robust and efficient security framework for all types of data.
Furthermore, data encryption is applied based on the state of the data, which is typically classified as either "data-at-rest" or "data-in-transit." Data-at-rest refers to information stored on devices like servers, laptops, or cloud storage. Encrypting this data, through methods like full-disk encryption or database encryption, protects it from being accessed if the physical device is stolen or compromised. Data-in-transit is information moving between networks, such as data sent over the internet or a private network. Encryption for data-in-transit, commonly implemented through protocols like HTTPS and VPNs, ensures that the information cannot be intercepted and read by eavesdroppers during its journey. A comprehensive data protection strategy requires the implementation of strong encryption for data in both of these states.
Ultimately, the importance of data encryption cannot be overstated. It is the core technology that enables secure e-commerce, private online communication, and the protection of national security secrets. Beyond just preventing unauthorized access, encryption is a crucial component for meeting regulatory compliance mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, which impose strict penalties for data mismanagement. As the volume and value of data continue to explode, the role of encryption will only become more critical. It is no longer just an IT function but a strategic business enabler, allowing organizations to innovate and leverage their data assets with confidence, knowing they are protected by a layer of mathematical certainty.
Explore Our Latest Trending Reports:
Proximity Access Control Market
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


