Zero Knowledge Proof: Verifying Transactions Without Revealing a Single Detail
Security and privacy now hold top priority in a fast-changing digital finance system, blockchain, and decentralized systems. Most users, developers, and regulators will require mechanisms of establishing the authenticity of transactions without revealing sensitive information. When using traditional verification, one may be asked to disclose information that may undermine confidentiality, which may be vulnerable and inefficient. Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) technology has become a new revolutionary answer, allowing to check the transactions, calculations, and identity assertions without showing one underlying detail.
Knowledge on the Concept of Zero Knowledge Proof
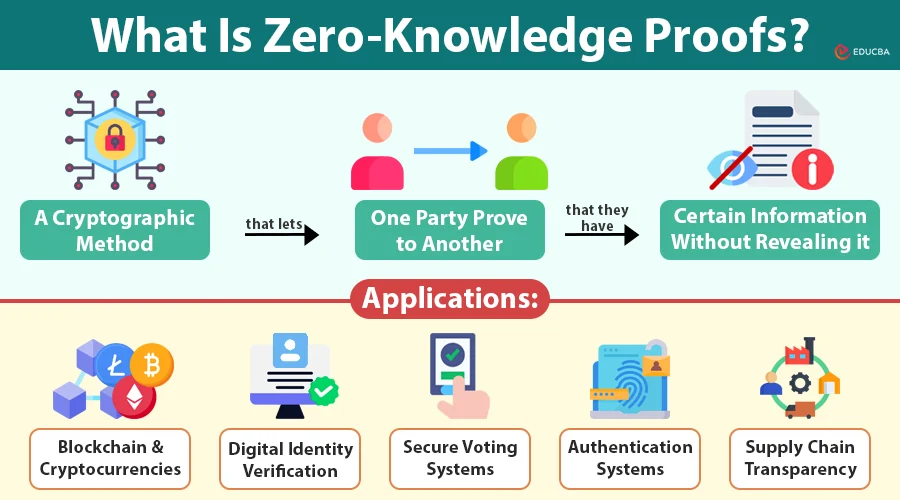
In its most simplistic form, a Zero Knowledge Proof is a type of proof in which one party, the prover, can convince another party, the verifier, that a specific statement is true, without revealing any other information. Such capability is a radical change of digital systems with a new level of privacy, security, and trust. ZKPs are confidential and can be verified with correctness unlike traditional verification techniques that require access to the underlying information.
The implication in blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystems can be extensive. ZKPs allow nodes and validators to verify the correctness of the transactions without being aware of the contents of the transactions. Equally, users can authenticate identity attributes including age, residency, or eligibility without showing personal documents in identity verification. This privacy/verifiability tradeoff is a decisive breakthrough to systems where both confidentiality and integrity are needed.
The Working of Zero Knowledge Proof
The mechanics of a Zero Knowledge Proof are complicated cryptographic protocols that validate three main properties, which are completeness, soundness, and zero-knowledge. Completeness guarantees that in the event of the statement being true, the verifier will be convinced by the evidence. The soundness ensures that, in the event that the statement is not true, the prover is unable to persuade the verifier of the truth of the statement. Zero-knowledge is such that the verifier gets to know nothing other than that the statement is true.
The use of succinct and non-interactive proofs in practical applications of ZKPs usually simplifies verification and improves efficiency. These proofs may be used to verify a whole block or a collection of transactions off-chain in blockchain applications and provide a small proof to the main network. This saves on the computing load, costs incurred in transactions and has high throughput without compromising security.
More complex applications are also possible, e.g. confidential smart contracts or a private voting system or a secure multiparty computation, all of which can be executed using the technology. In both cases, the prover proves to be compliant or right without exposing the sensitive data behind it, which guarantees privacy and trust at the same time.
Applicability of Zero Knowledge Proof in the real world
Zero Knowledge Proof is an adoption across various industries due to privacy, security and verifiability. In decentralized finance (DeFi), ZKPs can be used so that users can conduct confidential operations, allowing them to establish the authenticity and legality of funds without disclosing their balances or transaction history. The platforms can both ensure compliance with regulations and user privacy, which is essential in mainstream adoption.
The other key area where ZKPs can play an important role is blockchain scalability. Methods, such as zero-knowledge rollups, make use of ZKPs to bundle and convince a great deal of transactions off-chain, and present one proof back to the primary chain. This drastically enhances throughput, minimizes gas charges, and maintains the security assurances of the underlying blockchain. The uses include high-frequency trading to micro-payment systems and massive NFT platforms.
Outside the world of finance, Zero Knowledge Proof is also involved in secure identity verification. Users do not need to disclose the personal documents to prove such properties like age, residency, or certification. This allows privacy-sensitive KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) on online platforms, financial institutions and online services. Likewise, cloud computing and collaborative data analytics are also able to take advantage of ZKPs to guarantee that computations are correct even without revealing the underlying sensitive data.
Other new applications involve digital voting, supply chain verification and IoT networks. With digital voting, ZKPs can be sure that all votes are valid, but they are not going to identify voters. Supply chain systems can be used to determine authenticity and compliance of products without revealing proprietary information. The IoT devices have the potential of validating operations or sensor readings in a secure and private manner, thereby increasing the trust in distributed systems.
Strategic Implications and Advantages
There are a number of strategic benefits associated with the implementation of Zero Knowledge Proof. To begin with, it greatly improves the level of privacy since sensitive information is not disclosed during verification. Second, it enhances the security since cryptographic proofs eliminate the need to trust a mediator and less risk is exposed to a breach or a fraud. Third, it increases efficiency, especially when used in blockchain networks, where high-throughput and low-cost transactions are verified.
To developers and businesses, ZKPs offer an effective platform to develop systems that are both confidential and trustworthy. With the incorporation of ZKPs, the platforms will be able to provide users with secure and compliant services, increasing their adoption and use. The user is well assured in his or her interactions as they are sure that the data is safe even as verification is also trustworthy.
Strategically, the Zero Knowledge Proof technology is necessary when digital ecosystems become future-proofed. It takes the most urgent issues of privacy, regulatory compliance, and scalability into consideration and puts organizations in a better position to navigate an ever more complex digital environment. To technologists and investors, ZKPs are a vital innovation that is the foundation of privacy-preserving and verifiable digital infrastructures.
Moreover, the technology can be flexible to the new demands, including quantum computing, advanced cyber threats and new privacy rules. ZKPs guarantee that there is long-term resilience and trust on the digital platforms, financial systems, and blockchain networks by integrating verifiable confidentiality into the fundamental processes.
Conclusion
To sum up, Zero Knowledge Proof is the future of digital verification that allows individuals and businesses to verify statements, transactions, or identities without disclosing the data. The breakthrough solves major privacy, security, and scalability challenges, enabling decentralized systems, businesses and individuals to transact with a lot of confidence in a secure digital ecosystem.
Zero Knowledge Proof has applications in DeFi, blockchain scaling, verifying private identities, digital voting, supply chains and secure cloud computing. ZKPs offer a basis on which trust can be established in current digital systems by ensuring verifiability and confidentiality. To developers, investors, and technologists, it is crucial to know about ZKPs, as they are set to transform the world of safe, confidential and high-scale online interactions.
With the rapid rise in digitalization and the increasing concern over privacy, Zero Knowledge Proof presents a prospective solution which balances the elements of security, trust, and efficiency. It is not just a techno innovation but a basic platform on which next-generation platforms can be constructed with verification, privacy, and transparency living harmoniously. Digital systems may be made more confidential and reliable than ever before with ZKPs and are redefining the standards of secure interaction in the digital era.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


